Market Overview
The USA tire recycling market generated USD ~ million in 2024 and is forecast to reach USD ~ million by the end of the forecast window. Demand is fundamentally driven by rising end-of-life tire (ELT) generation, disposal bans and fees that keep material moving into permitted systems, and monetizable end-markets such as rubberized asphalt, molded rubber products, and tire-derived fuel. In 2023 benchmark, ~ of ELTs were reclaimed or recycled into end-use markets, reinforcing the depth of the domestic utilization base.
Dominance in the USA tire recycling ecosystem is typically concentrated in large population-and-freight corridors and heavy infrastructure states—where tire replacement volumes, hauler density, and proximity to off-takers create a cost advantage. Large metro logistics hubs and industrial belts support steady feedstock aggregation, while port-linked regions benefit where baled tires or processed outputs move internationally. On the demand side, states with robust roadworks pipelines and DOT openness to rubber-modified asphalt pull more crumb and powder into construction supply chains, and regions with cement kiln capacity provide stable TDF offtake.
Market Segmentation
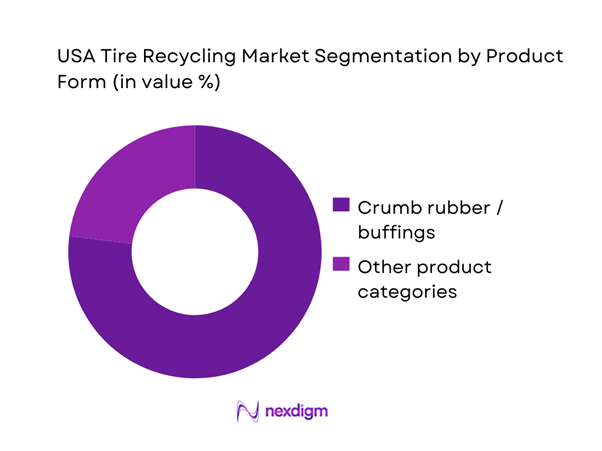
By Product Form
The USA recycled tire rubber value chain is segmented into crumb rubber and buffings, rubber powder, and other processed forms aligned to performance requirements. In 2024, crumb rubber and buffings held ~ share because it is the most versatile “workhorse” output: it feeds rubber-modified asphalt, molded rubber goods, and sports and leisure surfaces at industrial scale while using mature ambient and cryogenic grinding assets. Buyers also prefer crumb because quality specs such as particle size distribution, metal and fiber content, and moisture are relatively standardized and can be contractually enforced.
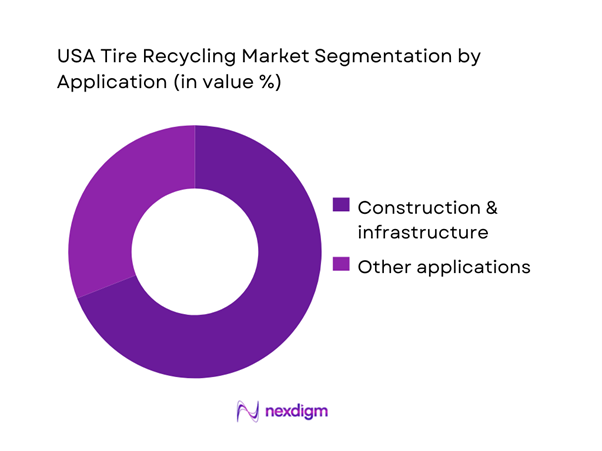
By Application
The market is segmented into construction and infrastructure, automotive, cement industry, sports and leisure, and others. 2024 shows construction and infrastructure at ~ share, largely because public works consume large tonnage per project and can absorb steady supply if DOT specifications and contractor practices are aligned. Rubber-modified asphalt and tire-derived aggregate tie directly to road resurfacing cycles, noise reduction, durability improvements, and stormwater and civil engineering use cases—giving recyclers a high-throughput outlet that is less fragmented than thousands of small molded-goods buyers.
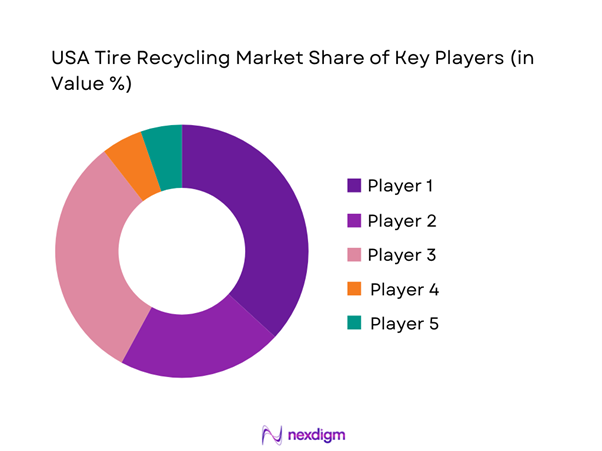
Competitive Landscape
The USA tire recycling market is consolidated around players with three capabilities: dense collection logistics, high-throughput processing, and anchored off-take channels such as DOT and asphalt, cement kilns, and industrial rubber compounders. At the national level, industry dynamics are shaped by a mix of scaled processors and regional specialists; the leaders differentiate through permitted footprint, quality assurance systems, long-term offtake contracting, and selective moves into higher-value outputs like reclaimed rubber and recovered carbon black.
| Company | Est. year | HQ | Core business model | Key outputs | Primary end-markets | Processing approach | Collection footprint | Differentiator (market-specific) |
| Liberty Tire Recycling | 1990s* | Pittsburgh, PA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lakin Tire | 1980s* | Buffalo, NY | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Emanuel Tire, LLC | 2000s* | Baltimore, MD | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ` | ~ |
| Entech, Inc. | 1990s* | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| CRM Rubber Manufacturers | 1980s* | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Tire Recycling Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
ELT Generation Intensity
End-of-life tire volumes in the U.S. stay structurally high because the underlying “wear engine” is national travel activity and a very large, highly urbanized vehicle base. Federal reporting shows Americans drove ~ vehicle-miles in the year, adding ~ miles versus 2023—more miles means more tread wear and replacement events across passenger, commercial, and off-road segments. In parallel, industry explanations note the U.S. generates more than ~ ELTs each year, anchoring a large, recurring feedstock stream for collection, processing, and end-use markets. The macro backdrop supports this intensity: U.S. GDP at USD ~ and population at ~ matter because high absolute output and population translate into high freight movement, commuting, and tire replacement cycles at scale. For tire recyclers, this volume certainty stabilizes inbound sourcing strategies and underwrites investments in shredding, granulation, and steel and fiber separation, because even small operational efficiency gains compound across very large annual ELT inflows.
Landfill Diversion Policies
State-level diversion architecture is a core demand-pull mechanism in U.S. tire recycling because it steers ELTs away from disposal and toward approved processors and end-markets. Industry bodies highlight that ~ states collect fees on the sale of new tires to fund end-of-life tire programs, backing enforcement against illegal dumping, cleanup of legacy stockpiles, and contracting structures that channel ELTs into permitted processing. The same policy ecosystem is reinforced by the stockpile reality check, with just under ~ ELTs remaining in U.S. stockpiles, keeping regulators focused on preventing new accumulations while pushing higher compliance for storage, transport, and processing. The macro context supports ongoing public-program capacity, as U.S. GDP of USD ~ indicates a large fiscal base where states can sustain environmental program administration and enforcement infrastructure when dedicated fee mechanisms exist. For the market, the key mechanism is not more tires, but more managed tires, reducing leakage and creating predictable offtake for registered processors.
Challenges
Permitting and Zoning Constraints
Scrap tire processing and storage are highly regulated locally because of fire risk, nuisance concerns, and environmental safeguards, so siting and scaling facilities often face municipal zoning limits and extended permitting pathways. Documented scrap tire fires have produced smoke plumes ~ high and extending ~, with fallout reported across ~ states, shaping public opposition and conservative permitting conditions for storage volumes and facility layouts. This is not an abstract risk, as just under ~ ELTs still remain in stockpiles nationwide, which typically trigger the tightest regulatory scrutiny and local resistance when new sites are proposed. From a macro standpoint, a population of ~ means siting conflicts are more likely in dense metros where tire generation is highest but land-use constraints and public objection are also strongest. The practical impact is that capacity additions can lag ELT generation, pushing recyclers to optimize throughput within existing footprints rather than rapidly expanding greenfield capacity.
End-Market Volume Swings and Revenue Instability
Tire recycling revenues depend on the stability of downstream offtake. When industrial fuel consumption, construction activity, or infrastructure procurement slows, recyclers can face inventory pressure even if inbound tires keep arriving. On the energy side, petroleum distillate demand stands at ~ barrels per day, while biofuel substitution reached ~ barrels per day, a fuel-pool shift that can influence industrial combustion choices and compliance strategies. On the infrastructure side, the road network spans ~ lane-miles, but material demand is driven by project pipelines, specifications, and DOT budgets that fluctuate by state. Meanwhile, inbound supply remains heavy, with more than ~ ELTs generated annually, so recyclers cannot turn off feedstock without risking illegal dumping or stockpile growth. Although U.S. GDP of USD ~ supports large end markets overall, cyclical slowdowns still transmit quickly to scrap commodities and recycled material demand.
Opportunities
Recovered Carbon Black Commercialization
Recovered carbon black is a growth opportunity because it moves the sector up the value chain from volume-driven diversion to specification-driven materials supply. The feedstock base is already large, with more than ~ ELTs generated each year, supporting continuous throughput for advanced processing routes when feedstock routing and inbound controls are established. Policy infrastructure supports better routing, as ~ states collect new-tire fees to fund ELT programs, strengthening permitted collection and reducing leakage. Environmental attention is rising, with ongoing research into tire impacts and compounds such as ~ increasing the premium on circular solutions that demonstrate controlled processing and documented outputs. The macro foundation, including GDP per capita at USD ~ and GDP at USD ~, supports industrial adoption of consistent secondary materials that meet performance and quality assurance requirements.
Advanced Devulcanization Technologies
Devulcanization is a market opportunity because it targets the hardest technical barrier in tire circularity while leveraging large ELT volumes and tightening environmental expectations. The U.S. generates more than ~ ELTs annually, ensuring raw material availability for pilots and scaled facilities. The opportunity is reinforced by unfinished cleanup burdens, with just under ~ ELTs remaining in stockpiles, keeping regulatory focus on managed, high-control solutions. Environmental scrutiny adds urgency, as increased focus on tire life-cycle impacts and compounds such as ~ favors technologies that document material transformation and output quality. The macro base, including GDP at USD ~ and population at ~, supports industrial experimentation and adoption in manufacturing, infrastructure products, and industrial goods.
Future Outlook
Over the next five to six years, the USA tire recycling market is expected to expand steadily as ELT generation remains structurally high, infrastructure spending and DOT openness to rubberized asphalt broaden durable demand, and circularity requirements create procurement pull for recycled inputs. The near-term shape of the industry will be defined by two competing forces: commodity outlets that absorb volume quickly, and higher-value recovery routes that can improve unit economics but require tighter specifications, permitting certainty, and bankable offtake.
Major Players
- Liberty Tire Recycling
- Lakin Tire
- Emanuel Tire, LLC
- Entech, Inc.
- BDS Tire Recycling
- CRM Rubber Manufacturers
- Genan, Inc.
- Rumpke Tire Recycling
- Champlin Tire Recycling, Inc.
- Lehigh Technologies
- Bolder Industries
- Klean Industries
- Contec
- ResourceCo
Key Target Audience
- Tire manufacturers and retreaders
- State DOTs and road authorities
- Asphalt producers and paving contractors
- Cement kilns, pulp and paper mills, and utility fuel managers
- Rubber and plastics compounders and molded rubber goods manufacturers
- Waste haulers and environmental services companies
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We construct an ELT ecosystem map across generators, haulers, processors, and off-takers, and define variables such as ELT generation density, transport radius economics, permitted capacity, and end-market price bands. This step is driven by structured desk research using association publications and state program disclosures, complemented by a standardized taxonomy for outputs.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We build the market using a bottom-up approach across processing categories and validate against published market totals. We normalize all quantities to consistent units and reconcile value using realization logic, with scenario bands for commodity-linked volatility.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate hypotheses through structured interviews with recyclers, haulers, asphalt contractors, cement kiln fuel buyers, and state tire program stakeholders. These inputs refine utilization assumptions, yield rates, contamination penalties, and contracting structures for major outlets.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We triangulate secondary datasets with primary findings to finalize segmentation logic, competitive benchmarking, and forward outlook. Outputs are stress-tested through sensitivity checks around transport costs, policy shifts, and end-market substitution risks.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Taxonomy, Market Sizing Approach, Bottom-Up & Top-Down Validation, Conversion Assumptions (tires-to-tons), Primary Interview Coverage (processors/haulers/off-takers), Data Triangulation, Sensitivity Analysis (gate-fee vs commodity), Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Evolution and Genesis
- Industry Timeline
- Business Cycle Linkage
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Growth Drivers
ELT Generation Intensity
Landfill Diversion Policies
Infrastructure Demand for Rubber-Modified Asphalt and TDA
Fuel Substitution Economics
OEM Sustainability and Circularity Targets
Recovered Carbon Black Adoption - Challenges
Permitting and Zoning Constraints
End-Market Price Volatility
Environmental and Health Scrutiny
Feedstock Contamination and Quality Variability
Logistics and Transportation Costs
Fire Risk and Compliance Management - Opportunities
Recovered Carbon Black Commercialization
Advanced Devulcanization Technologies
Expansion of DOT Specifications
Electrification-Driven NVH Rubber Demand
Digital Traceability and EPR Models - Trends
Mesh Grade Standardization
Circular Procurement Mandates
Long-Term Offtake Contracting
Integration of Thermal and Mechanical Processing - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Realization, 2019–2024
- By Feedstock Source (in Value %)
Passenger and Light Truck ELTs
Commercial Truck ELTs
Off-the-Road Tires
Specialty Tires
Mixed Bales - By Collection and Sourcing Channel (in Value %)
Tire Dealers and Retailers
Fleet Depots
Municipal and Transfer Stations
Auto Dismantlers
Industrial Generators
Cleanup Stockpiles - By Processing Pathway (in Value %)
Ambient Grinding
Cryogenic Grinding
Shredding and Chipping (TDF/TDA)
Devulcanization and Reclaimed Rubber
Pyrolysis - By Output Product Form (in Value %)
Crumb Rubber and Buffings
Rubber Powder (Mesh Grades)
Tire Chips and Shreds
Tire-Derived Aggregate
Recovered Steel
Recovered Carbon Black - By End-Use Offtake Market (in Value %)
Rubber-Modified Asphalt
Molded Rubber Goods
Sports and Leisure Surfacing
Civil Engineering and Stormwater
Cement, Pulp and Paper, Utility Fuel
Exports - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market Positioning of Major Players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (annual ELT throughput, collection network density, processing yield split, product quality and mesh capability, end-market diversification, long-term offtake coverage, compliance and fire-risk controls, advanced recovery readiness)
- SWOT of Major Players
- Price and Realization Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Liberty Tire Recycling
Lakin Tire
Emanuel Tire
Entech
BDS Tire Recycling
CRM Rubber Manufacturers
Genan
Rumpke Tire Recycling
Champlin Tire Recycling
Lehigh Technologies
Bolder Industries
Globarket
TDJ Group
Klean Industries
- Demand & Utilization
- Procurement & Contracting
- Regulatory & Specification Requirements
- Pain Points & Decision Drivers
- Decision-Making Process
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Realization, 2025–2030


