Market Overview
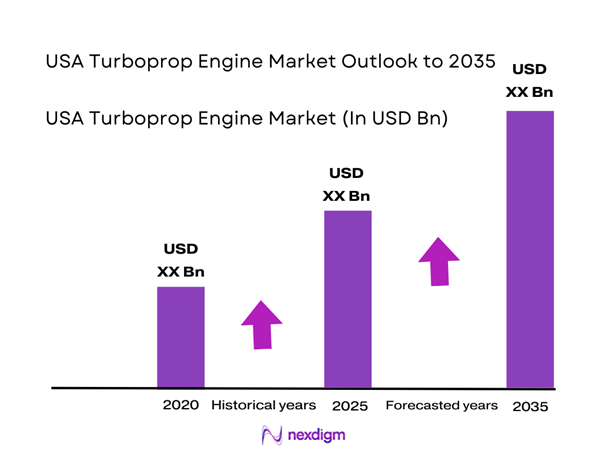
The USA Turboprop Engine market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady demand driven by regional aviation, defense modernization, and specialized aerial operations. In recent periods, fleet utilization increased across cargo, training, and surveillance applications, supporting consistent engine deployment levels. Engine deliveries remained stable, supported by replacement demand and incremental fleet expansion. Maintenance intensity also rose as aging aircraft required higher service frequency. Technological upgrades and fuel efficiency improvements influenced procurement cycles. The market continues to benefit from diversified usage profiles across civil and government aviation segments.
The market is primarily concentrated in regions with strong aviation infrastructure, established MRO networks, and high regional connectivity demand. Southern and Western states host dense operational bases due to favorable flying conditions and logistics activity. Defense aviation hubs also contribute significantly through training and surveillance operations. Presence of OEM facilities, component suppliers, and overhaul centers strengthens ecosystem maturity. Supportive regulatory frameworks and sustained fleet renewal programs further reinforce regional demand concentration across key aviation corridors.
Market Segmentation
By Application
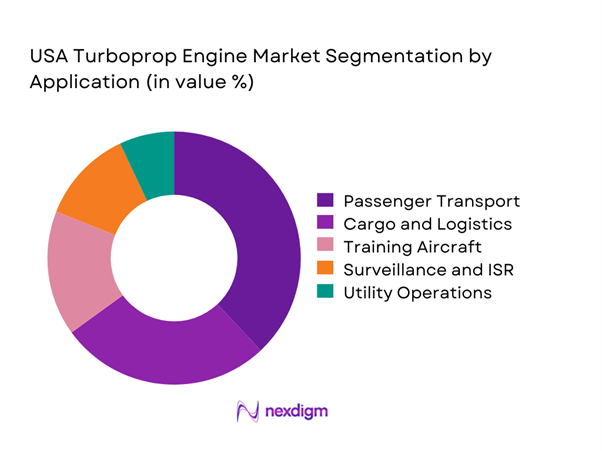
The application-based segmentation is dominated by passenger and cargo operations, supported by regional connectivity requirements and short-haul route economics. Passenger turboprops remain essential for serving low-density routes where jet operations are uneconomical. Cargo and feeder services continue expanding due to e-commerce growth and time-sensitive logistics demand. Training and special mission aircraft also contribute steadily, supported by military and aviation academy requirements. Surveillance and utility roles add incremental demand, particularly from border security and disaster response agencies. Overall, application diversity ensures stable engine utilization across multiple operational profiles.
By End-Use Industry
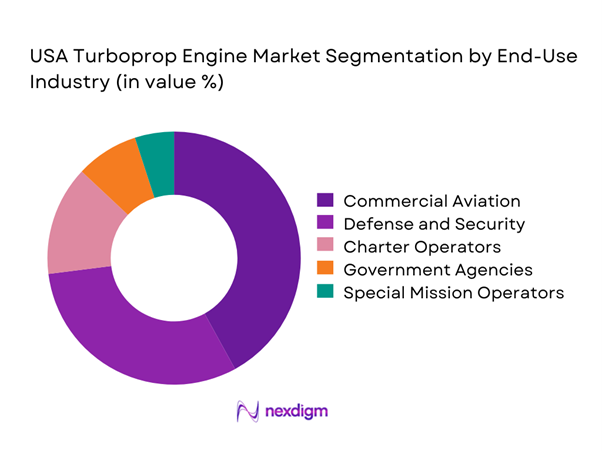
End-use industry segmentation is led by commercial aviation operators, followed closely by defense and government users. Regional airlines depend heavily on turboprop fleets for cost-efficient operations and network connectivity. Defense usage remains stable due to training, reconnaissance, and transport requirements. Charter operators and special mission service providers contribute moderate demand, particularly in remote and underserved regions. Government agencies increasingly rely on turboprops for surveillance and emergency response missions. This diversified end-user base supports consistent market activity and reduces reliance on a single demand source.
Competitive Landscape
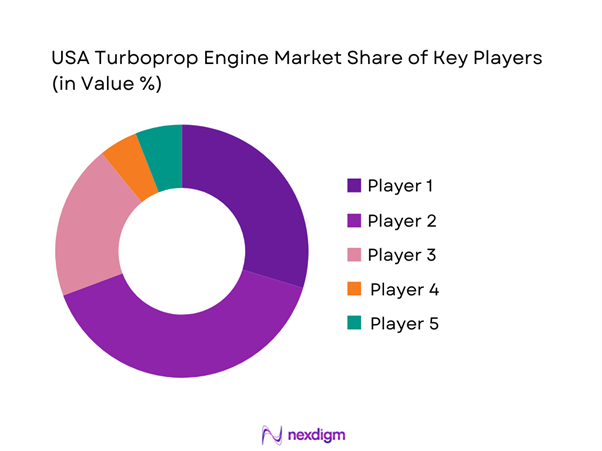
The competitive landscape is characterized by a limited number of established engine manufacturers with strong technological capabilities and global service networks. Market participants compete on performance reliability, maintenance intervals, and lifecycle support offerings. Long-term service agreements and aftermarket capabilities play a critical role in customer retention. Entry barriers remain high due to certification complexity and capital intensity. Continuous innovation and regulatory compliance define competitive positioning across the industry.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Pratt & Whitney Canada | 1928 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GE Aerospace | 1917 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Honeywell Aerospace | 1906 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rolls-Royce | 1906 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Safran Aircraft Engines | 1905 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
USA Turboprop Engine Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising demand for regional air connectivity
Regional air connectivity continues expanding due to limited ground transport alternatives across dispersed population centers. Airlines increasingly deploy turboprops to maintain route profitability on low-density sectors with consistent passenger demand. Government-backed regional connectivity programs support aircraft utilization across underserved airports nationwide. Improved fuel efficiency enhances operating economics compared with regional jets on short routes. Fleet renewal programs emphasize turboprop adoption due to favorable lifecycle performance. Increasing air travel frequency supports sustained engine utilization across regional networks.
Rising demand for regional air connectivity
Airport infrastructure development enables increased turboprop movements across secondary and tertiary locations. Airlines prioritize fleet flexibility to adapt to fluctuating passenger volumes. Turboprop aircraft offer operational advantages in short runway environments. Improved passenger comfort has strengthened traveler acceptance of turboprop flights. Regional tourism growth also supports demand for short-haul air services. Combined factors reinforce long-term growth momentum for turboprop engine deployment.
Challenges
High capital and maintenance costs
High acquisition costs remain a major barrier for smaller operators entering turboprop operations. Maintenance expenses increase as engines age and require frequent inspections. Spare parts availability can impact operational continuity for fleet operators. Skilled maintenance labor shortages add further cost pressures. Compliance with strict aviation safety standards elevates lifecycle expenses. These cost factors influence fleet replacement and expansion decisions significantly.
High capital and maintenance costs
Operators must balance operational efficiency against rising ownership expenditures. Long overhaul cycles increase aircraft downtime and planning complexity. Financing limitations affect fleet modernization among regional carriers. Maintenance scheduling inefficiencies can reduce aircraft availability. Rising material and labor expenses continue to pressure operating margins. Cost containment remains a critical strategic focus across the industry.
Opportunities
Growth in regional and short-haul aviation
Regional air mobility demand continues expanding due to urban congestion and remote connectivity needs. Turboprops provide optimal economics for short-haul routes with moderate passenger loads. Infrastructure upgrades support increased regional air traffic movements. Airlines increasingly prioritize flexible fleet strategies to serve dynamic markets. Government-backed connectivity initiatives further stimulate regional aviation growth. These factors create sustained opportunities for turboprop engine deployment.
Growth in regional and short-haul aviation
Tourism development in secondary cities increases demand for efficient regional aircraft operations. Turboprops enable direct connections without hub dependency. Environmental efficiency enhances their appeal amid sustainability considerations. Fleet renewal cycles favor modern turboprop platforms. Consistent utilization strengthens aftermarket and service revenue opportunities. The segment remains a cornerstone for future market expansion.
Future Outlook
The USA turboprop engine market is expected to maintain stable growth supported by regional connectivity expansion and defense modernization programs. Advancements in fuel efficiency and digital engine monitoring will enhance operational performance. Fleet replacement cycles are expected to accelerate as older aircraft retire. Demand from cargo and special mission operations will remain resilient. Overall market fundamentals indicate steady long-term development.
Major Players
- Pratt & Whitney Canada
- GE Aerospace
- Honeywell Aerospace
- Rolls-Royce
- Safran Aircraft Engines
- MTU Aero Engines
- RTX Corporation
- StandardAero
- Textron Aviation
- IHI Corporation
- Magellan Aerospace
- Aviadvigatel
- Turbomeca USA
- Honeywell International
- GE Aviation Systems
Key Target Audience
- Commercial aircraft operators
- Regional airline companies
- Defense and military aviation units
- Government aviation departments
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Federal Aviation Administration and Department of Defense
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key operational, technological, and regulatory variables influencing turboprop engine demand were identified. Fleet composition, utilization rates, and replacement cycles were evaluated. Application-specific performance requirements were mapped. Market boundaries were defined based on usage and certification scope.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Industry data was structured using bottom-up assessment methods. Segmentation was developed across application, end-use, and operational categories. Demand drivers and constraints were analyzed through historical performance indicators. Comparative analysis ensured consistency across data sets.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through expert discussions with aviation engineers, operators, and maintenance professionals. Assumptions were tested against operational realities. Feedback loops refined demand assumptions and usage trends. Market behavior was cross-verified across multiple data points.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into a coherent analytical framework. Data inconsistencies were reconciled through triangulation. Narrative insights were aligned with quantitative indicators. Final outputs were structured to support strategic decision-making.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and aircraft engine scope alignment, turboprop segmentation by power class and aircraft type, bottom-up fleet-based market sizing, OEM and MRO revenue attribution modeling, primary interviews with engine OEMs and operators, triangulation using FAA fleet data and defense procurement records, assumptions on utilization cycles and replacement rates)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and operational profiles
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and aftermarket dynamics
- Regulatory and certification environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising demand for regional air connectivity
Expansion of cargo and feeder aircraft operations
Lower operating cost versus turbofan aircraft
Modernization of military trainer and ISR fleets
Improved fuel efficiency and emissions performance - Challenges
High capital and maintenance costs
Limited production volumes compared to jet engines
Regulatory certification complexity
Supply chain constraints for critical components
Competition from advanced turbofan aircraft - Opportunities
Growth in regional and short-haul aviation
Increasing use of turboprops in defense ISR missions
Adoption of digital engine health monitoring
Hybrid-electric propulsion development
Aftermarket and MRO service expansion - Trends
Shift toward lightweight and fuel-efficient engines
Increased adoption of FADEC systems
Rising demand for low-emission propulsion
Integration of predictive maintenance analytics
OEM focus on lifecycle service contracts - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Commercial aviation
General aviation
Military and defense
Special mission and surveillance - By Application (in Value %)
Passenger transport
Cargo and logistics
Training aircraft
Surveillance and ISR
Utility and special purpose - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Single-shaft turboprop
Free turbine turboprop
Hybrid-assisted turboprop - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial airlines
Charter and regional operators
Defense and homeland security
Aerial services and utility operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Conventional engine control
FADEC-enabled systems
Digitally connected and predictive maintenance engines - By Region (in Value %)
Northeast
Midwest
South
West
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (engine power rating, fuel efficiency, time between overhaul, installed base, aftermarket support, certification status, pricing, technological maturity)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Pratt & Whitney Canada
GE Aerospace
Honeywell Aerospace
Rolls-Royce Holdings
Safran Aircraft Engines
RTX Corporation
MTU Aero Engines
Textron Aviation
General Electric Aviation Systems
Honeywell International
Magellan Aerospace
Aviadvigatel
IHI Corporation
Turbomeca USA
StandardAero
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


